
What are some of the tissues that make up the spine? The coccyx also provides a third point of contact when a person sits down. These muscles aid in defecation, support for female reproductive organs and help you move your legs.
The coccyx’s main job is to serve as an attachment site for muscle insertion. Like the sacrum, the coccyx is a highly durable, weight-bearing structure. Issues with the sacrum will impair your ability to walk, sit and stand. The sacrum bears the weight of the upper body and is integral to walking and other leg functions. It is highly durable by necessity multiple key muscle groups attach to the sacrum. They connect to the hips on the left and right to create a circular structure called the pelvic girdle. Sacrumīelow the lumbar spine is the sacrum, a triangular bone of five fused vertebrae (S1-S5). Injuries from 元-L5 affect both the legs and hips, and they may also lead to numbness in the feet. Most spinal column issues are in the lumbar section because of the weight the lumbar spine carries. Together, they create a slight outward curve to the spinal column in contrast to the inward curve of the thoracic section. These are the largest of the vertebrae, and they excel at absorbing stresses from lifting and carrying loads. The lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5) serve to support the neck and thoracic regions. However, the causes of the pain do tend to be more severe than causes for pain in the cervical or lumbar sections. Pain in this area usually lasts only a short time and isn’t known to be particularly painful. Each of the 12 pairs of ribs connects to one of the 12 thoracic vertebrae. This section consists of 12 vertebrae (T1-T12) that connect to ribs and protect the heart and lungs as its primary function. C1 and C2 allow us to turn, tilt, nod and pivot our heads. The cervical spine has the greatest range of motion of all the sections.

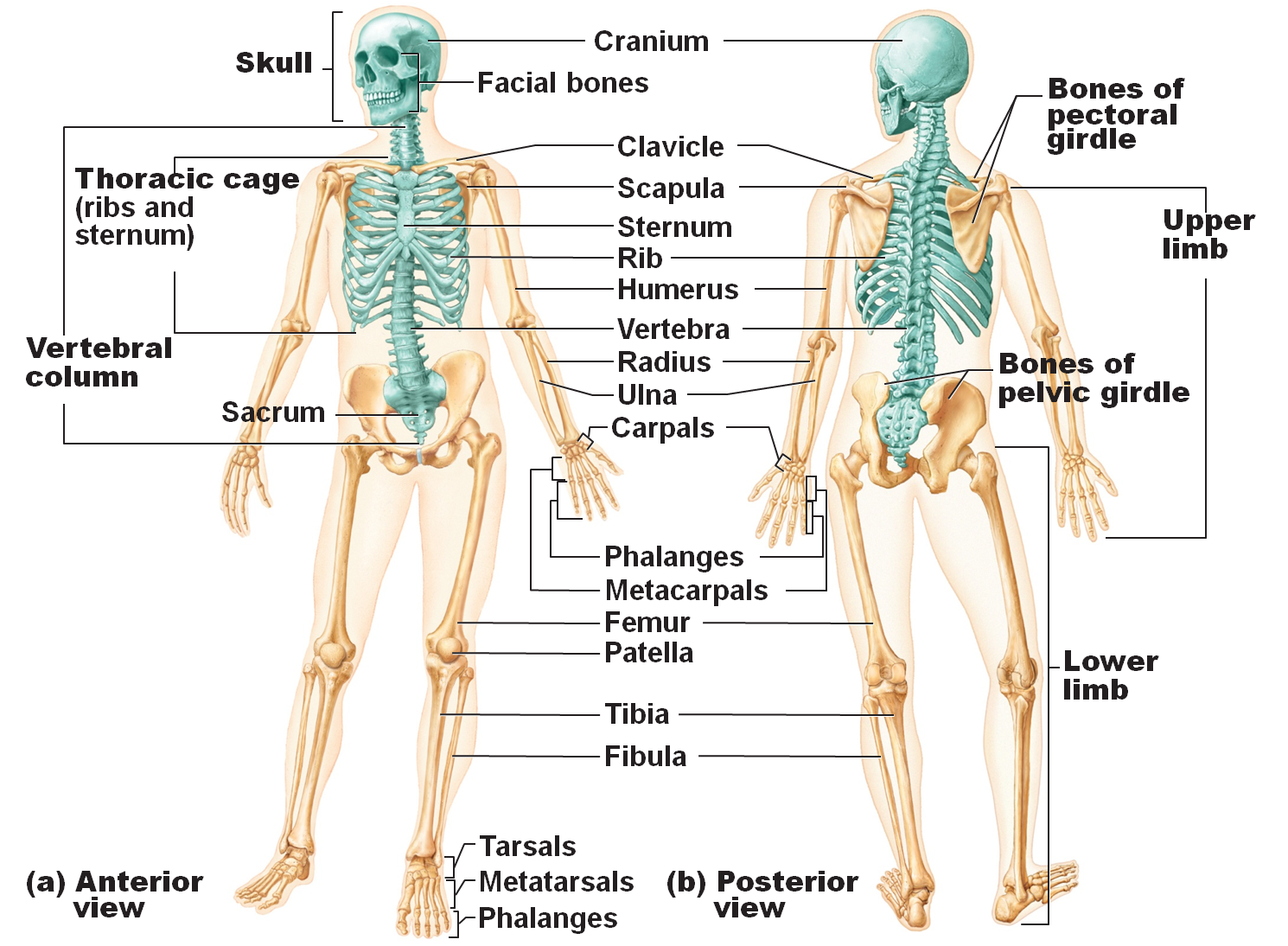
The aptly-named “atlas vertebra” supports the skull, similar to how the mythological Atlas holds up the world. Seven cervical vertebrae (C1-C7) make up the cervical spine section. The parts of the spine are broken into these five sections of vertebrae: Cervical spine (neck) What are the five main parts of the spine? They naturally get thinner as we age and cause us to lose height, and make us more susceptible to injury. These are the discs that can be bulging, herniated or thinning. Unfortunately, spinal injuries may result in some messages never reaching their destination.ĭiscs between the vertebrae act as cushions to prevent bones from grinding against each other. The spine is a column of bones that work together to house the spinal cord, our nervous system’s “superhighway.” Messages travel from the brain, down the spine and out through the peripheral nerves, think smaller highways and city streets. Here, we break down the main parts of the spine. Understanding the parts of the spine can give you a better idea of what to look out for when it comes to pain or injury. These bones make up the spinal column that holds your body upright, allows it to twist and bend and provides a safe channel for nerves to run from the brain throughout your body. The spine is composed of 33 bones, called vertebrae, divided into five sections.
#Parts of spine series
It is an incredibly complex series of bones, joints and other tissues. There are only 7 cervical vertebrae but 8 cervical nerves because cervical nerve 1 (C1) comes out rostral to the first cervical vertebra and cervical nerve 8 (C8) comes out caudal to the seventh cervical vertebra.Your spine is unlike any other part of your body.

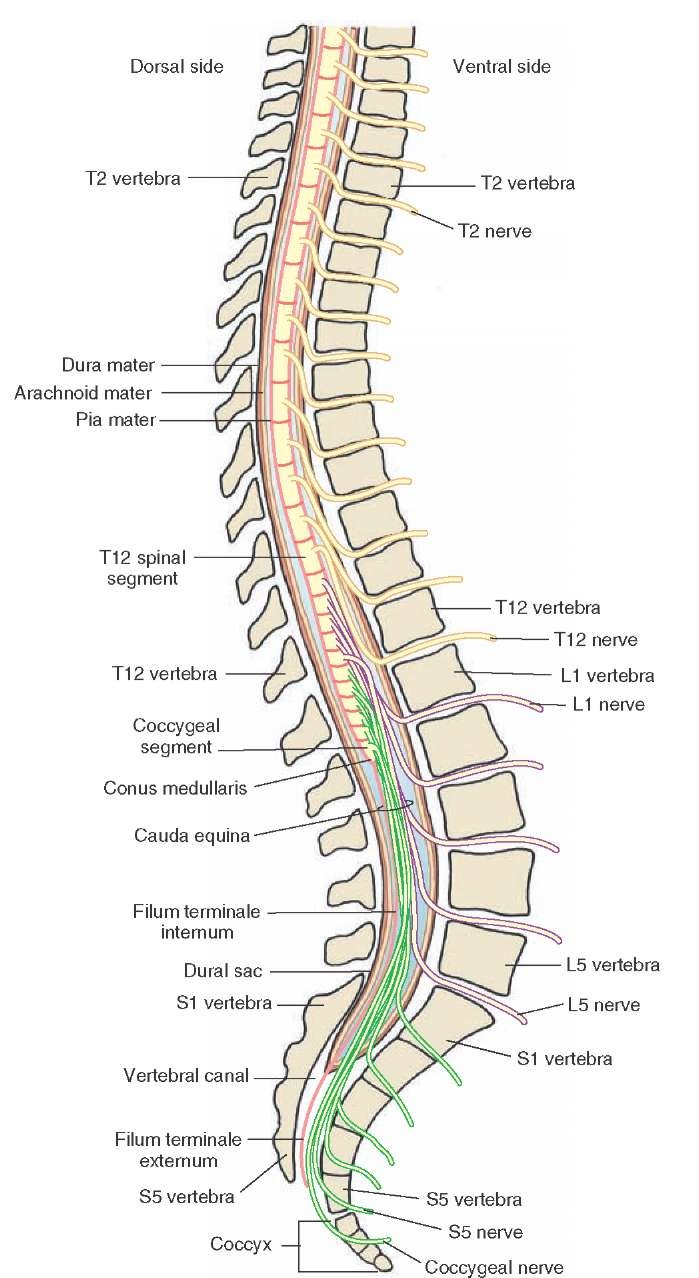
Why are there 8 cervical pairs instead of 7? Its three major roles are to relay messages from the brain to different parts of the body, to perform an action, to pass along messages from sensory receptors to the brain, and to coordinate reflexes that are managed by the spinal cord alone. In this regard, what are the different parts and functions of the spinal cord? The spinal cord (and brain) are protected by three layers of tissue or membranes called meninges, that surround the canal. Subsequently, question is, what is the ventral aspect of the spinal cord? Ventral roots consist of efferent fibers that arise from motor neurons whose cell bodies are found in the ventral (or anterior) gray horns of the spinal cord. The spinal cord is divided into four different regions: the cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral regions (Figure 3.1). The gray matter is the butterfly-shaped central part of the spinal cord and is comprised of neuronal cell bodies.Īlso to know is, what are the sections of the spinal cord? They feature fissures (anterior) and sulci (anterolateral, posterolateral, and posterior). Cross section It shows four surfaces: anterior, posterior, and two lateral.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
